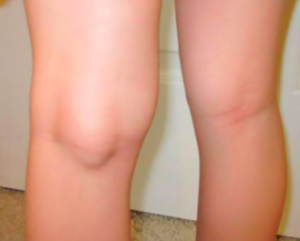
What causes a baker’s cyst?
Baker’s cysts occur when synovial fluid is forced out from the knee joint and into the back of the knee, producing a swollen cyst. This can occur due to:- A knee injury
- Cartilage (meniscus) damage to the knee joint
- Knee arthritis (osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis)
- Other causes of knee joint inflammation
What are the symptoms?
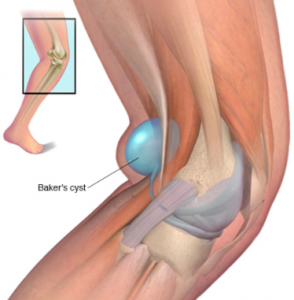 Symptoms of a baker’s cysts can include:
Symptoms of a baker’s cysts can include:
- Pain in the back of the knee
- Inflammation
- Redness
- Bruising
- Tenderness
- Stiffness in the knee joint
 How is it treated?
How is it treated?